索引管理 API
# 索引管理 API
# 前言
索引管理的 API 提供了单个索引的管理(创建和删除)、别名管理、索引设置、定义 Mapping、Reindex、索引模板、索引收缩等功能。
# 单个索引的管理
# 创建索引
# 创建索引的最基本形式,没有指定 Mapping
PUT test_index
# 创建带 setting 和 Mapping 的 books 索引
PUT books
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"book_id": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"name": {
"type": "text"
}
}
},
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 3, # 指定了 3 个主分片
"number_of_replicas": 1 # 指定了一个副本分片
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
创建索引的限制有以下几个:
- 只能是小写字母。
- 不能包含
\,/,*,?,",<,>,|,(空格),,,#等字符。 - 7.0 之后的版本不能再包含
:(冒号)字符了。 - 不能以
-,_,+开头。名字不能是.或者..。 - 不能长于 255 字节。需要注意的是某些字符是需要多个字节来表示的。
# 删除索引
# 删除一个索引
DELETE test_index
2
# 索引别名管理
当业务需求发生改变,而不得不创建一个新索引来代替旧索引的时候,我们必须更新应用服务(后端代码)的索引名称,使用索引别名可以解决这个问题。假设应用中用 test 别名指向旧索引 test_old,在创建新索引 test_new 并将 test_old 的数据迁移到 test_new 后,我们可以将 test 索引别名指向 test_new,这样可以做到在新旧索引间的无缝切换。
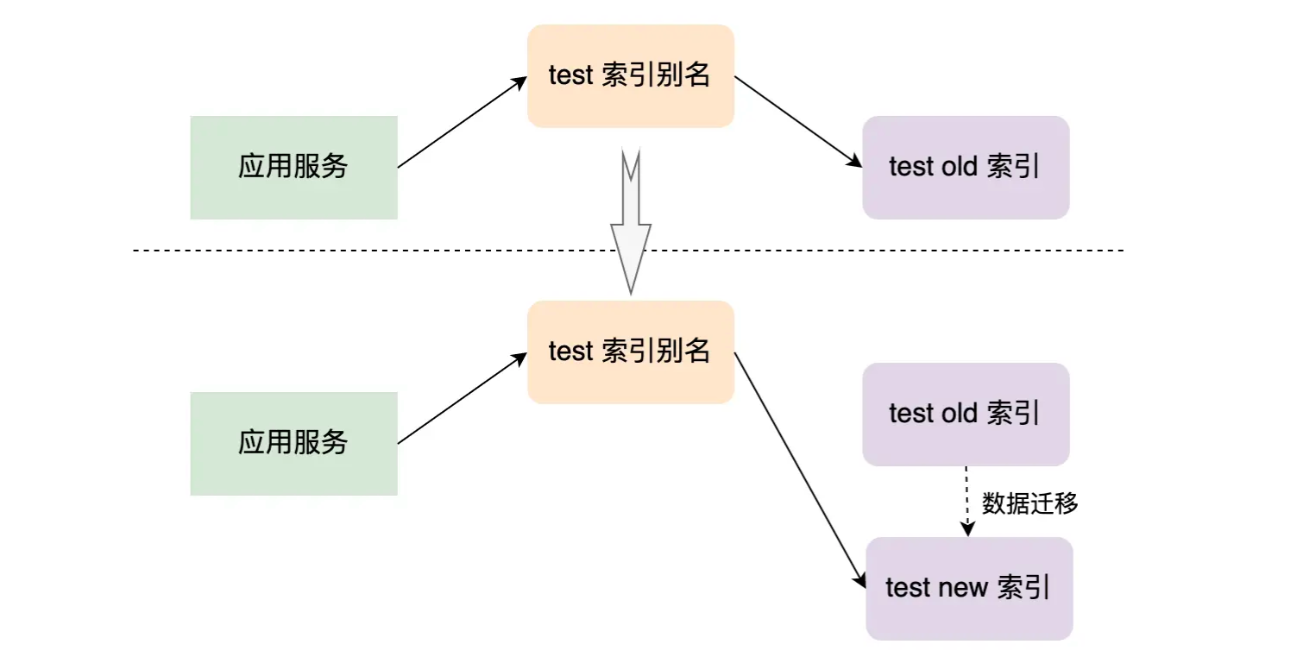
(索引别名 - 以 test 为例)
别名就是一个索引另外的名字,其就像一个软连接或者快捷方式。每个索引可以有多个别名,而不同的索引也可以使用相同的别名,这样使得不同的别名可以适用于不同的情景。
# 别名创建
# 为 test1 索引创建了 "alias1" 别名
POST /_aliases
{
"actions" : [
{ "add" : { "index" : "test1", "alias" : "alias1" } }
]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 别名删除
# 删除了索引 test1 的别名 "alias1"
POST /_aliases
{
"actions" : [
{ "remove" : { "index" : "test1", "alias" : "alias1" } }
]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 别名重命名
别名重命名的操作是先将原先的别名删除了,然后再创建新的别名。这操作是原子的,不需担心别名不指向索引的短暂时间。
POST /_aliases
{
"actions" : [
{ "remove" : { "index" : "test1", "alias" : "alias1" } },
{ "add" : { "index" : "test1", "alias" : "alias2" } }
]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 关联多个索引
# 将别名 alias1 指向了索引 test1、test2 。
POST /_aliases
{
"actions" : [
{ "add" : { "indices" : ["test1", "test2"], "alias" : "alias1" } }
]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
更多的别名使用示例可以参考官方文档 (opens new window)。
# 索引设置
在创建索引的时候,可以在 "settings" 字段中指定索引的设置。number_of_shards 和 number_of_replicas 是索引非常重要的两个配置,设置它们值的示例如下:
PUT test_index
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 3, # 指定了 3 个主分片
"number_of_replicas": 1 # 指定了一个副本分片
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
也可以动态修改索引的配置,其示例如下:
PUT /test_index/_settings
{
"number_of_replicas": 2
}
2
3
4
但要注意的是,number_of_shards 设定后是无法改变的,要修改索引的分片数量可以通过 Reindex API 或者收缩索引的 API 做处理。
# 定义索引的 Mapping
在创建索引的时候可以设置索引的 Mapping(使用 "mappings" 字段)。其示例如下:
PUT test_index
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"test_id": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
如果增加了某些需求,想要增加索引 Mapping 的设置,其示例如下:
PUT test_index/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"test_name": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
需要注意的是,在 Mapping 中已经定义好的字段是不能修改的,如果尝试修改将会返回错误提示。
# Reindex API
对于已经创建过的 Mapping ,既不能修改已经定义过的字段类型,同时也不能改变分片的数量。而如果需求上必须要我们修改,就可以使用 Reindex API 来解决这个问题。
首先创建一个新的索引,使其 Mapping 等设置满足新的需求,然后将数据从旧的索引中迁移到新的索引。具体步骤如下:
# 创建新的索引,并且满足需求
PUT test_index_reindex
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"test_id": { "type": "keyword" },
"test_name": { "type": "text" }
}
}
}
# 执行 reindex 操作
POST _reindex
{
"source": { "index": "test_index" },
"dest": { "index": "test_index_reindex" }
}
# 在迁移数据后的 test_index_reindex 索引中获取数据
GET test_index_reindex/_doc/1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
需要注意的是,如果索引中的数据很多,并且是需要同步返回的情况下,在 Kibana 中执行这个操作可能会发生超时的现象。可以使用 wait_for_completion=false 参数来进行异步操作,其示例如下:
# 异步地执行 _reindex
POST _reindex?wait_for_completion=false
{
"source": { "index": "test_index" },
"dest": { "index": "test_index_reindex" }
}
# 结果
{
"task" : "26d0dAjcRYygigd0shfz5w:35995695"
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
异步的 reindex 操作返回的结果将会是个 task id,可以使用 Task API 查看这个任务的情况:
GET /_tasks/26d0dAjcRYygigd0shfz5w:35995695
Reindex API 还提供很多丰富的参数和操作示例,可以参考官方文档 (opens new window)。
# 索引模板
可以使用 Index templates 按照一定的规则对新创建的索引进行 Mapping 设定和 Settings 设定。需要注意的是,索引模板只在索引被新创建时起作用。
创建一个模板:
PUT /_index_template/my_tmp1
{
"index_patterns" : ["tmp_*"], # 以tmp_ 开头的索引都引用这个模板
"priority" : 1, # 指定优先级, 数值越大优先级越高, 这个模板就越先被应用
"template": {
"settings" : {
"number_of_shards" : 3
},
"mappings": {
"date_detection": false
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# 打开和关闭索引
当我们需要执行某些操作的时候,需要关闭索引或者打开索引,可以使用 _close API 和 _open API 来关闭或者打开索引。
关闭索引的操作开销很小,并且会阻塞读写操作,关闭后的索引不再允许执行打开状态时的所有操作。关闭和打开一个索引的示例如下:
# 关闭索引
POST /test_index/_close
# 打开索引
POST /test_index/_open
2
3
4
5
# 判断索引是否存在
可以使用 Exists API 来判断一个索引是否存在,其示例如下:
HEAD test_index
如果索引存在,那么返回的 HTTP 状态码为 200,不存在的话为 404。更多关于 Exists API 的使用示例,可以参考官方文档 (opens new window)。
# 收缩索引
如果一开始创建的索引其分片太多,可以使用收缩索引的 API 将索引收缩为具有较少主分片的新索引。
收缩后的新索引的主分片数量必须为源索引主分片数量的一个因子。例如,源索引的主分片分配了 12 个,那么收缩后的新索引的主分片数只能为 1、2、3、4、6。
在进行索引收缩前需要进行以下操作:
- 源索引必须只读。
- 源索引所有的副本(主分片也行,副分片也行)必须在同一个节点上,也就是在这个节点上必须有这个索引的所有数据,不管分片数据是主分片的还是副分片的。
- 源索引的状态必须为健康状态(green)。
下面示例:将拥有 12 个主分片、2 个副本分片的索引(test_index)收缩为拥有 3 个主分片和 1 个副分片的索引(test_index_new)。
# 第一步:创建原索引
先创建索引 test_index,设置 number_of_shards = 12,number_of_replicas = 2:
# 创建原索引(测试用)
PUT test_index
{
"mappings": {
"properties": { "test_name": { "type": "keyword"} }
},
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 12,
"number_of_replicas": 2
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# 第二步:收缩前准备
下面将索引 test_index 所有的主分片转移到节点 my_ndoe_1 上,并且设置索引的副本分片数量为 0、设置这个索引为只读状态:
PUT /test_index/_settings
{
# 分片分配到 my_node_1 节点
"index.routing.allocation.require._name": "my_node_1",
"index.number_of_replicas": 0,
"index.blocks.write": true
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 第三步:开始进行收缩
OK,这个时候 test_index 满足了收缩索引的 3 个条件了,下面开始进行收缩:
POST /test_index/_shrink/test_index_new
{
"settings": {
"index.number_of_replicas": 1,
"index.number_of_shards": 3,
"index.routing.allocation.require._name": null, # 系统随机分配分片
"index.blocks.write": null # 不阻塞写操作
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
如上示例,我们设置了新索引的主分片数量为 3,每个主分片的副本数量为 1,并且这些分片是系统自动、随机分配的,不阻塞新索引的写操作。
更多关于收缩索引 API 的使用参数和示例,可以参考官方文档 (opens new window)。
# 参考资料
(完)
