解构赋值
# 解构赋值
# 数组解构赋值
# 基本用法
将值从数组中取出,赋值给其他变量。这是一个拷贝过程,原数组和元素本身不会被改变。
let [a, b, c] = ['a', 'b', 'c'] // ["a", "b", "c"]
1
# 可以是任意可遍历的对象
赋值的元素不仅是数组,它可以是任意可遍历的对象。
let [a, b, c] = "abc" // ["a", "b", "c"]
let [one, two, three] = new Set([1, 2, 3]) // [1, 2, 3]
1
2
2
# 使用场景
# 1)循环体中使用,配合 Object.entries() (opens new window)
- 每次遍历得到一个数组,该数组的元素是给定对象自身可枚举属性的键和值
- 接下来的解构操作本质上就是解构的基本用法
let user = {
name: 'zhangsan',
age: 13
}
for (let [key, value] of Object.entries(user)) {
console.log(`${key}:${value}`)
}
// name:zhangsan
// age:13
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 2)循环体中使用,配合 Map 对象 (opens new window)
let user = new Map()
user.set('name', 'zhangsan')
user.set('age', 13)
for (let [key, value] of user.entries()) {
console.log(`${key}:${value}`)
}
// name:zhangsan
// age:13
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 跳过赋值元素
如果想忽略数组的某个元素对变量进行赋值,可以使用逗号来处理。
let [mon, , wed] = ['Monday', 'Tuesday', 'Wednesday', 'Thursday', 'Friday', 'Saturday', 'Sunday']
console.log(wed) // Wednesday
1
2
3
2
3
# rest 参数
可以使用 rest 参数(形式为 ...变量名)来接受赋值数组的剩余元素,不过要确保这个 rest 参数是放在被赋值变量的最后一个位置上。
let [mon, tues, ...rest] = ['Monday', 'Tuesday', 'Wednesday', 'Thursday', 'Friday', 'Saturday', 'Sunday']
console.log(mon) // Monday
console.log(tues) // Tuesday
// rest 是个数组
console.log(rest[0]) // Wednesday
console.log(rest[1]) // Thursday
console.log(rest.length) // 5
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 默认值
如果数组的内容少于变量的个数,没有分配到内容的变量会是 undefined。
let [firstName, lastName] = []
console.log(firstName) // undefined
console.log(lastName) // undefined
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
也可以给变量赋予默认值,防止 undefined 的情况出现。
let [firstName = 'Guest', lastName = 'Anonymous'] = ['Kobe']
console.log(firstName) // Kobe
console.log(lastName) // Anonymous
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
# 对象解构赋值
# 基本用法
左侧的变量名要和右侧对象中存在的 key 名一致,但是顺序无需一致。
let options = {
title: 'Menu',
width: 100,
height: 200
}
let {title, width, height} = options
console.log(title) // Menu
console.log(width) // 100
console.log(height) // 200
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
提取出来的值也可以赋值给其它的变量名。
let options = {
title: 'Menu',
width: 100,
height: 200
}
let {title: t, width: w, height: h} = options
console.log(t) // Menu
console.log(w) // 100
console.log(h) // 200
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# rest 运算符
可以像数组一样,只提取指定的属性,将其他可以暂存到一个变量下,这就要用到 rest 运算符(形式为 ...变量名)了。
let options = {
title: 'Menu',
height: 200,
width: 100
}
let {title, ...rest} = options
console.log(rest.height) // 200
console.log(rest.width) // 100
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 默认值
赋值的过程中也可以指定默认值。
let options = {
title: 'Menu'
}
let {width = 100, height = 200, title} = options
console.log(title) // Menu
console.log(width) // 100
console.log(height) // 200
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 嵌套对象
如果一个 Array 或者 Object 比较复杂,它嵌套了 Array 或者 Object,那只要被赋值的结构和右侧赋值的元素一致就好了。
就像这样:
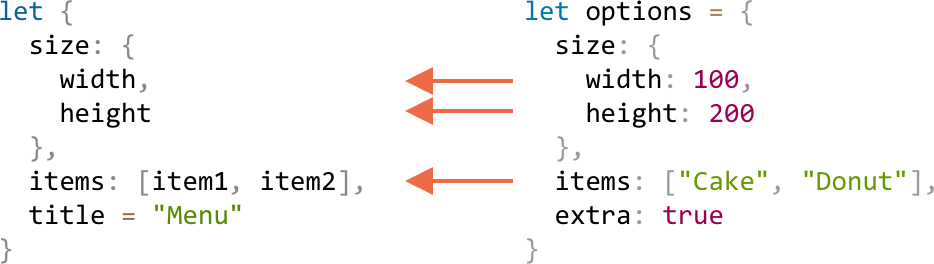
(嵌套对象的解构赋值)
let options = {
size: {
width: 100,
height: 200
},
items: ["Cake", "Donut"],
extra: true // 不提取这个值
}
let {
size: {
width,
height
},
items: [item1, item2],
title = 'Menu' // 默认参数
} = options
console.log(title) // Menu
console.log(width) // 100
console.log(height) // 200
console.log(item1) // Cake
console.log(item2) // Donut
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# 字符串解构赋值
本质上就是把字符串当做是数组来解构。
let str = 'hello'
let [a, b, c, d, e] = str
console.log(a, b, c, d, e)
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
# 参考资料
(完)
